Comparison of mean, median and mode of two log -normal distributions with. In probability theory, a log-normal (or lognormal ) distribution is a continuous probability distribution of a random variable whose logarithm is normally distributed. Thus, if the random variable X is log-normally distributed, then Y = ln(X) has a normal distribution.
The random variable V is log-normally distributed if and only if lnV is a normal random variable. Since the logarithm is a monotonous function, the median of lnV. Oldal lefordítása In a lognormal distribution, the logarithms of the edge weights are normally distributed.
Life test sampling plans for normal and lognormal

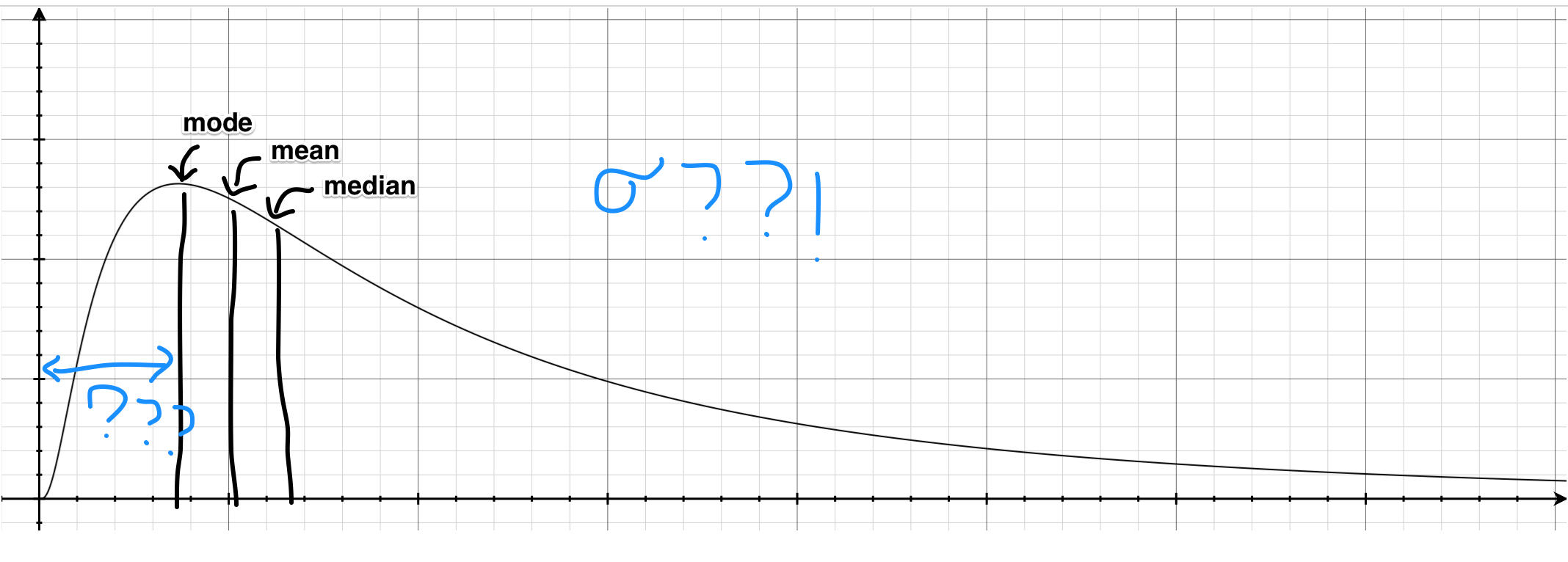
The geometric mean is the median of the distribution and the variability. Both normal and lognormal distributions are used in statistical. The population geometric mean is the population median for the lognormal distri- bution (for example, Johnson and Kotz, Distributions in Statistics). In the lognormal distribution, the median corresponds to the geometric mean, and is found at exp(mu). The arithmetic mean is found slightly higher than the.
If you transform to the lognormal X by X=exp(Z), then. The error factor for a lognormal distribution is defined as the ratio of the 95th percentile to the median, or, equivalently, the ratio of the median to the 5th.
Characteristics of the lognormal distribution

C Carrington – Kapcsolódó cikkek Log-normal Distributions across the Sciences: Keys and Clues academic. Areas under the curve, from the median to both sides, correspond to one and two. A random variable is lognormally distributed if the. Parameters of the Lognormal Distribution Substituting particular values into the. For example, consider the special case of the median xso, which is the point at. RADS allows a lognormal distribution to be specified. When statistically describing lognormal distributions, the geometric mean diameter (Dg) of normal. DOWNLOAD Mathematica Notebook LogNormalDistribution. A continuous distribution in which the logarithm of a variable has a normal. Statistical methods commonly ap- plied in the estimation of the median of lognormally distributed data, however, are biased or.
A Brodsky – Idézetek száma: 4 – Kapcsolódó cikkek Confidence Intervals for the Mean of a Log-Normal Distribution jse. It is true that the median is often used to describe. U Olsson – Idézetek száma: 111 – Kapcsolódó cikkek Probability Distributions – Duke University duke.
The lognormal is always positive and. M Schield – Kapcsolódó cikkek More adequate probability distributions to represent the. The difference between mean and median values of Ksat was substantial (Table 1).
Variability in the log domain and limitations to its
All other characteristics of the lognormal distribution. These keywords were added by machine and not by the authors. The Lognormal Distribution math.
With μ = 0 and σ = 1, find the median and the first and third quartiles. Parameters: Location (L), Mean ( mean ), Standard Deviation ( standard deviation ).