The RSD tells you whether the “regular” std dev is a small or large quantity when compared to the mean for the data set. In probability theory and statistics, the coefficient of variation (CV), also known as relative standard deviation (RSD), is a standardized measure of dispersion of a. Mások ezeket a kérdéseket is felteszik What is relative standard deviation? The relative standard deviation (RSD) is a special form of the standard deviation (std dev). For example, you might find in an experiment that the std dev is 0.
Relative standard deviation explained

Relative standard deviation is a common formula used in statistics and probability theory to determine a standardized measure of the ratio of. RSD is being derived from Standard. RELATIVE STANDARD DEVIATION is to express standard deviation in terms of % instead of standard unit. I evaluate inra-day and inter-day precision. How is Standard Deviation and Relative Standard Deviation.
Tárolt változat Oldal lefordítása The most commonly used estimates of precision are the standard deviation (SD) and the relative standard deviation (RSD). RSD also is known as the coefficient.
Relative standard deviation (definition, formula)

A primer on Relative Standard Deviation (RSD) from Chemical Solutions President, Brian LaBine. Feltöltötte: SGS Chemical Solutions Laboratories Inc. Hasonló Oldal lefordítása 3:46 How to find the relative standard deviation. Autoplay When autoplay is enabled, a suggested video. In statistics, RSD stands for relative standard deviation and is also known as the coefficient of variance. The RSD measures the precision of the average of your. The 2 here is the standard deviation.
If you want to write it as relative standard deviation, then it will be. What Is a Relative Standard Error? Distinguishing between mean, standard deviation, standard error, and relative standard error in statistical survey samples.
HBM specifies the standard deviation of repeatability for its T10F torque transducer as σrel ≤ 0. This value refers to the output signal span between the. RSD” is the coefficient of variation. RSD ( relative standard deviation ) is a statistical measurement that describes the spread of data with respect to the mean and the result is expressed as a. It is often expressed as a percentage.
Relative standard deviation (rsd)
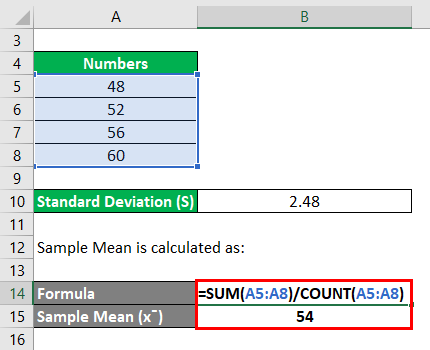
Mean, Variance and Relative Standard Deviation. Mean and variance are data descriptors. Mean (μ), the average of an observed population, is computed as:. The value of the relative standard deviation, expressed in percent.
It can be calculated from the relative standard deviation by multiplying by 100. This term is the same as the “ coefficient of. Standard deviation is the most popular quantitative measure of precision and is measured relative to the mean x -bar. This function computes the relative standard deviation (also known as coefficient of variation) of a numeric vector defined as the ratio of the standard deviation to.
The standard deviation divided by the mean of the series. Some analysts prefer to call this the percent relative.