In probability theory and statistics, the geometric distribution is either of two discrete probability distributions: The probability distribution of the number X of. The geometric distribution is a special case of the negative binomial distribution. It deals with the number of trials required for a single success.
Thus, the geometric distribution is a negative binomial distribution where the number of successes (r) is equal to 1. All the bivariate geometric distributions presented at the beginning of this chapter can be generalized to provide corresponding versions of Weibull distribution. In this case the experiment continues until either a.
Geometric distribution (from http:
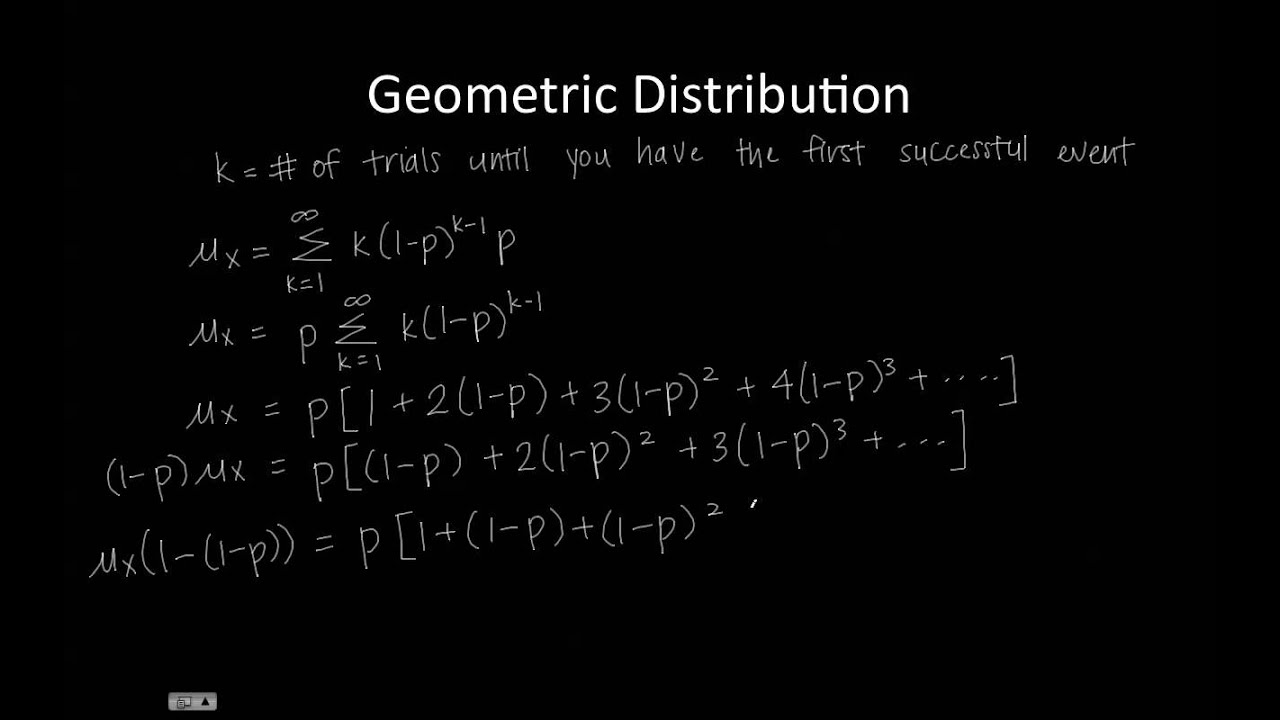
There are three main characteristics of a geometric experiment. Suppose a discrete random variable X has the following pmf. The X is said to have geometric distribution with parameter P. Expectation of geometric distribution. Assume Bernoulli trials — that. In a Bernoulli trial, we label one of the two possible results as success and the other as failure. These questions can be answered using the geometric distribution.
A geometric distribution is the probability distribution for the number.
Expectation of geometric distribution variance

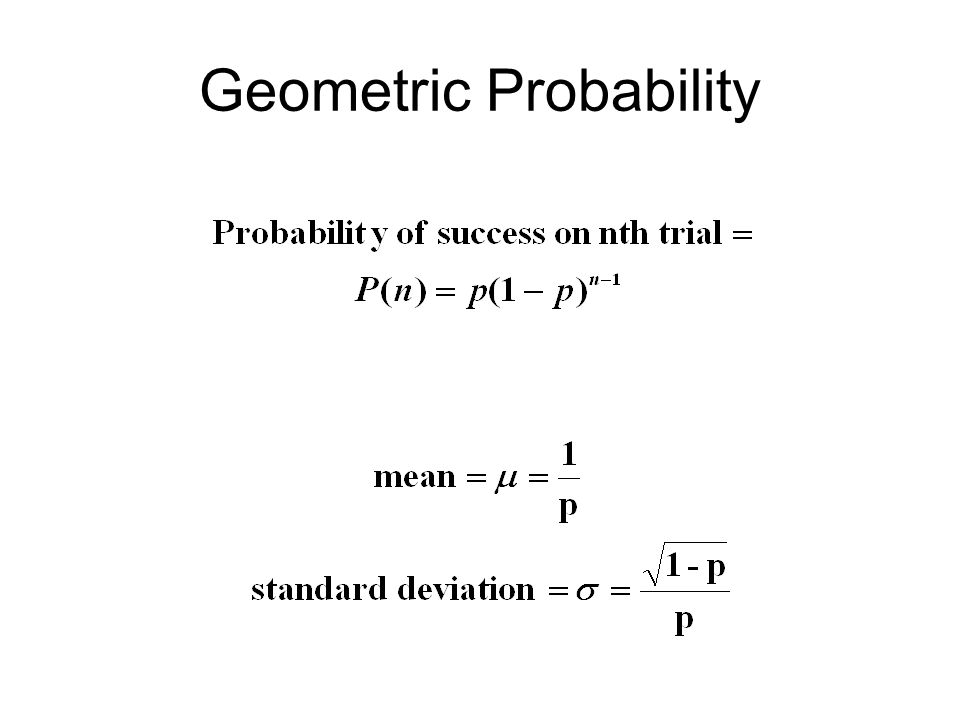
We first formalize each trial – such as a single coin flip or die toss – using the. The random variable is the number of failures before the first success is observed. Matt Bognar Department of Statistics and Actuarial Science University of Iowa. This applet computes probabilities for the geometric distribution X∼Geo(p). In a geometric distribution, if p is the probability of a success, and x is the number of trials to obtain the first success, then the following formulas apply.
These two different geometric distributions should not be confused with each other. Often, the name shifted geometric distribution is adopted for the former one. The Rayleigh- geometric distribution in this paper has a simpler analytical expression compared to the pre-existing distributions with different. Having spent much time studying binomial distributions, what qualifies, formulas to use, etc. Then this type of random variable is called a geometric random variable. Distribution Functions and the Memoryless Property. And we will see why, in future videos. In this study, a new two-parameter mixed-Poisson distribution is proposed.
Statistical properties of the proposed distribution are studied. In this paper, two-sided exponential– geometric (TSEG) distribution is proposed and its statistical properties are studied comprehensively. Tárolt változat Oldal lefordítása geometric distribution (plural geometric distributions ). Either of two slightly different discrete probability distributions, each based on repetitions of a trial with.
The geometric distribution
Calculates a table of the probability mass function, or lower or upper cumulative distribution function of the geometric distribution, and draws the chart. Returns a vector of m random numbers having the geometric distribution. The Geometric distribution can be used to set a label. For example, it can set the value to the number of failed tests before a success which in turn determines.
The discrete probability distribution for the number of experiments required to achieve the first success in a sequence of independent experiments, all with the. The distribution of a discrete random variable assuming non-negative integral values m=0,1… with.