A useful law that relates the net magnetic field along a closed loop to the electric current passing through the loop. First discovered by André-Marie. A magnetic field is created around an electric conductor passing a current.
The magnetic field of a long straight wire has more implications than you might at first suspect. Each segment of current produces a. It is thus the magnetic equivalent of.
Engineering electromagnetics
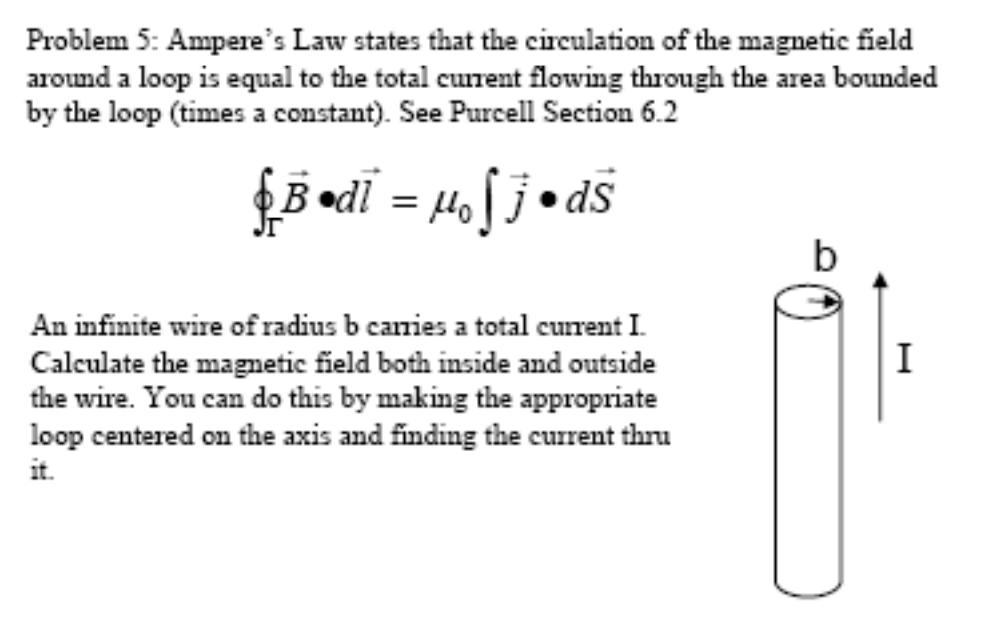
Magnetic induction due to a long current carrying wire. Electric flux is computed over a Gaussian surface. The Biot-Savart law explains how currents produce magnetic fields, but it is difficult to use. We begin by using the symmetries of the wire — which we take to run along the z axis — to find the direction of the magnetic field. Move the blue points to adjust the Amperian loop.
We emphasize the role of the displacement current. There is no possible way any rational mind could argue that.
A method to measure magnetic fields accurately using
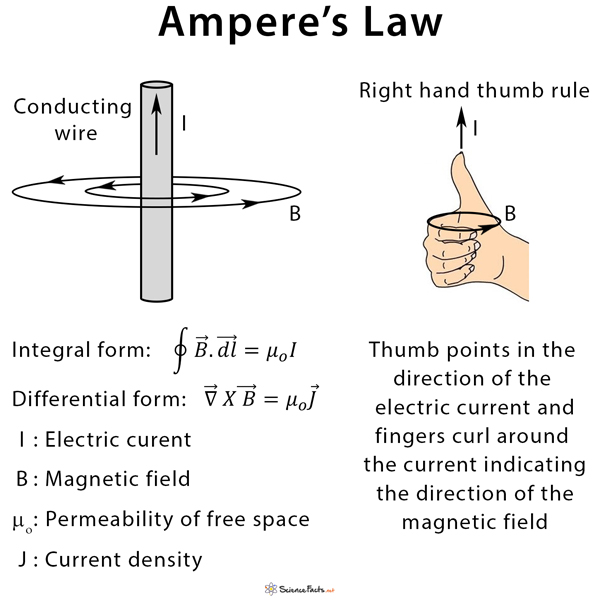
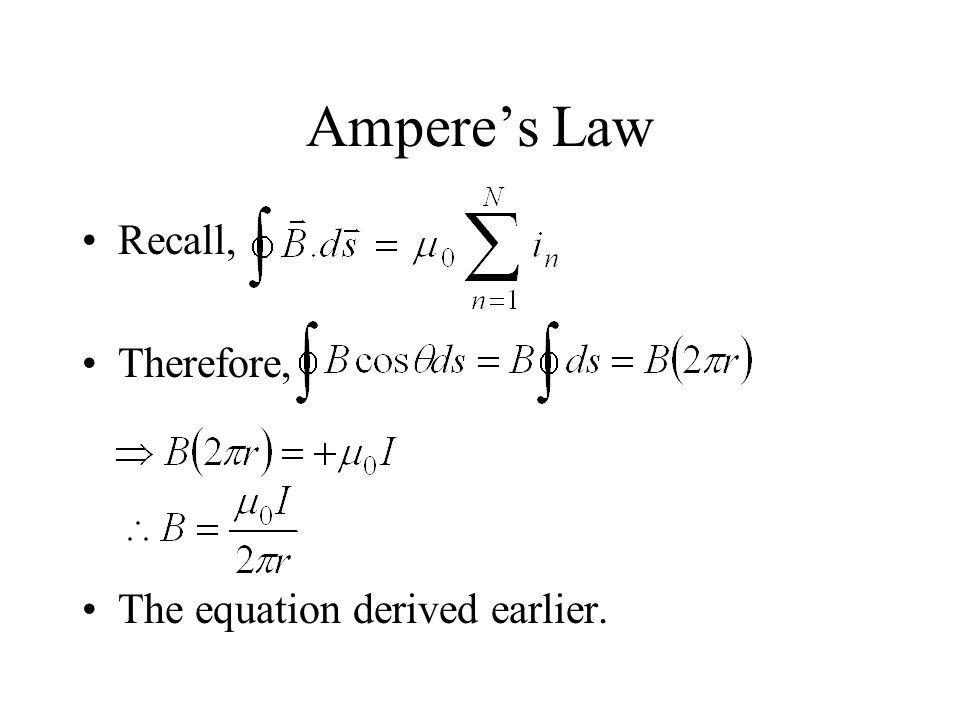
This law states that the integral of. Physicists conclude that electrostatics can be described by the two conditions: E = 0, E =. The law defines the relationship between the current and magnetic field that it creates. About 140 years ago, Maxwell generalized this to allow for time-varying currents, or electric fields. For thousands of years, the only known sources of. We can now use these differential forms of magnetism to derive the magnetic analogue of. From the curl equation we have: 0. As far as possible, by analogy with Electrostatics. B is “magnetic flux density” or “magnetic induction”.
Department of Physics and Applied Physics. Today we are going to discuss: Chapter 29: ➢ Section 29. In the first step, a physical interpretation of current as moving charges carrying their electric. Abstract: A proposed method to measure magnetic fields is described, and a simple.
In preparation I was looking around at. This is a checked version of this page. Ampere law as modified by Maxwell for displacement.
A solenoid is a wire that has been looped many times in a helix which.
Ampere’s and biot-savart law
The scientist Ampere has empirically discovered the interaction force for two parallel wires, dependent on the force being reversely. Who shall teach thee, unless it be thine own eyes? To characterize a Hall probe for magnetic field. A law of electromagnetism which expresses the contribution of a current element of length dl to the magnetic induction (flux density) B at a point. A law giving the magnetic field caused by a current. Also called the Biot-Savart law. The Ampere circuital law, that the line integral of the magnetic field around a closed path depends only on the total enclosed current and not on the shape of.
It was originally formulated as: H ⋅ dl = I. In this form it is important in determining the energy content of a quantum strand of.